Project Reference
Gridchain
Crowd-balancing using Blockchain Technology
When people talk about „Blockchain in Energy“ they usually have „P2P Trading“ in mind – either between households or between wholesale energy traders. P2P trading between households was intensively marketed by the „Brooklyn microgrid“ and today about 50 start-ups across Europe pursue this business idea. P2P trading between wholesale energy traders is one of PONTON’s blockchain-related focus (à Enerchain). In contrast, the operation of gas and power grids is much more a „B2B“ model, as grid processes are very detached from consumers perception („the power comes out of the socket“) and even energy engineers require decades to fully comprehend in full detail, how grids do actually operate.
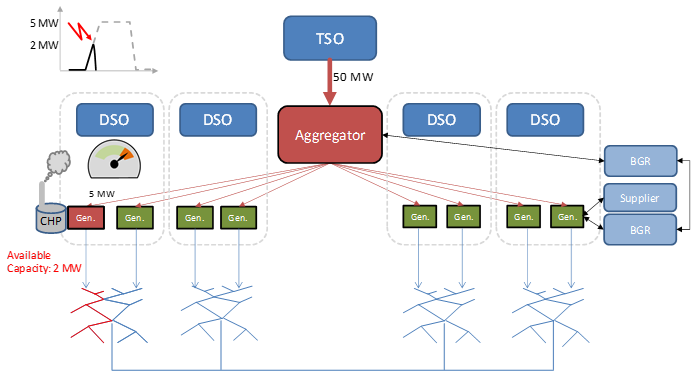
However, also for grid operators there is potential for blockchain technology as it enables to facilitate processes that are distributed across organisations like TSOs (transmission system operators), DSOs (distribution system operators), aggregators (pooling the generation capacity of a large number of small units), suppliers, balancing responsible parties, balancing group coordinators, etc. A typical TSO-driven processes is to request balancing energy in order to keep grid load and frequency stable. This process has been practised for a long time now and it is deeply entrenched in all participants´ IT systems. On the other hand, DSOs continuously monitor load of the distribution grid and take measures to keep it stable at the local level. They need to coordinate planned and unplanned local outages and exceptional congestion situations within local grids due to an increased share of generation from renewables – which is expected to further increase in the future.
As load volatility increases there is also an increased need to coordinate DSO and TSO processes. Of course, this is already done today, but there is still room for further standardisation and improvement. Traditionally, balancing power was purely requested from large generation units owned by grid operators themselves, but after energy-related services were unbundled, balancing power is provided today by an increased number of generators with a decreased minimal requirement for generation capacity. Today, there are aggregators that pool thousands of generation assets, which reside in local grids scattered across the country and even across national borders. If 100 MW of balancing power is requested today, it might be distributed across 5-10 medium-sized generators. If the same volume will be requested in 5 years´ time, it might be distributed across 100-1.000 small generators, including batteries operated by households. For example, California allows already today to participate in the balancing process with only 0,5 MW generation capacity.
This trend of fragmentation and acceleration of processes will require a re-thinking of inter-process communication among all parties involved. It is not only important for all individual market participants to communicate bilaterally, it is also required to get smaller participants, like aggregators and generators, involved in market processes at a high level of reliability and responsiveness. Security of supply will always be the benchmark for process design and quality. And due to the high number of participants it would be desirable to drive down cost and the duration of the settlement process for delivering balancing power. All-in-all this sounds like an ideal breeding ground for the blockchain!
As a consequence, PONTON was requested by a group of Austrian DSOs to explore possibilities of leveraging blockchain technology for grid process integration. The results are mind-blowing:
- we created an integrated process that coordinates requesting of balancing power between TSOs, DSOs, aggregators, and generation units within seconds
- we enabled DSOs to interact with the balancing request process in congestion situations well before the delivery period and not just at the stage when the generation load is actually ramped up by the aggregator,
- we provided a means to inform aggregators about adjusting their merit order list depending on short-term load signals,
- we brought down settlement time from > 1 month to just 15 minutes.
PONTON has developed an innovative pilot software based on blockchain technology that simulates future processes for real-time grid management, called Gridchain. The next step will be to practically test this process „in the field“ with a selection of market participants, i.e., a coalition of the willing. Moreover, Gridchain is a contribution to the European standardisation of inter-process communication when designing smart grids of the future.
Gridchain Video (in German):